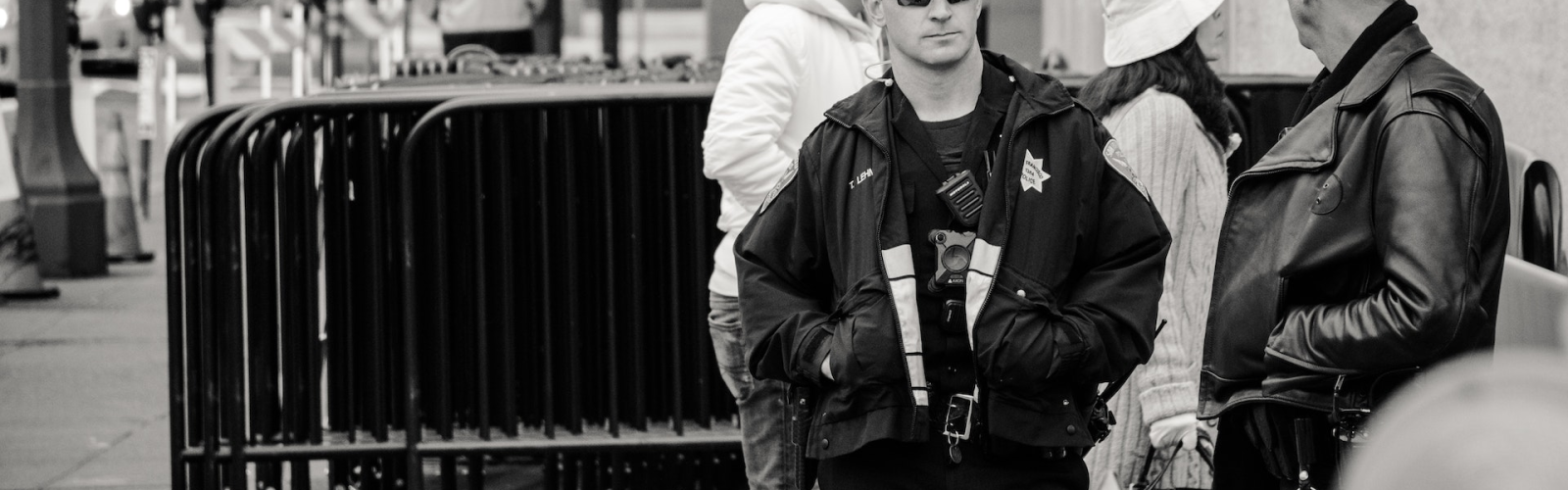
Germany is a country known for its strict security measures, and this extends to its security control systems as well. The country has a highly sophisticated security control system that ensures the safety and security of its citizens, visitors, and assets.
One of the primary components of the German security control system is the use of CCTV cameras. These cameras are installed in public places, government buildings, and high-security areas. The footage from these cameras is closely monitored by security personnel, who are trained to identify any suspicious activities and respond quickly to potential threats.
Another important aspect of the German security control system is the use of biometric technology. This includes facial recognition software, which is used in airports, train stations, and other high-security areas to quickly and accurately identify individuals who may be a security threat. This technology is also used in border control to monitor and track the movement of people across the country's borders.
In addition to CCTV cameras and biometric technology, the German security control system also includes access control measures. This includes the use of security gates, keycard systems, and other physical barriers to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive areas. Security personnel are also trained to conduct thorough checks on individuals entering these areas, including bag checks and body scans.
One unique aspect of the German security control system is its emphasis on privacy protection. While the system is designed to maintain security and prevent potential threats, it also takes into account the privacy rights of individuals. For example, the country's data protection laws ensure that any personal information collected by security measures is only used for security purposes and is not shared with unauthorized parties.
Privacy protection is an essential component of any modern society, and Germany is known for its strong emphasis on privacy rights. The country has a comprehensive set of data protection laws that ensure individuals' privacy is respected and their personal data is used only for legitimate purposes.
One of the primary pieces of legislation governing data protection in Germany is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which is a European Union regulation that came into effect in 2018. The GDPR provides a set of rules and guidelines for the processing of personal data, including how data is collected, stored, and used.
Under the GDPR, individuals have the right to know what data is being collected about them, why it is being collected, and who it is being shared with. They also have the right to access their personal data and request that it be corrected or deleted if necessary. Companies and organizations are required to obtain individuals' explicit consent before collecting and processing their personal data.
In addition to the GDPR, Germany has its own set of data protection laws that go above and beyond the EU regulations. For example, the Federal Data Protection Act (BDSG) regulates the processing of personal data by federal authorities and private companies operating in Germany. The law provides additional protections for sensitive data, such as health and financial information.
Overall, privacy protection is taken very seriously in Germany, and the country's data protection laws are among the strongest in the world. These laws ensure that individuals' privacy rights are respected and that their personal data is used only for legitimate purposes, while still allowing companies and organizations to operate and provide essential services.
Overall, the security control system in Germany is highly effective in maintaining the safety and security of its citizens, visitors, and assets. While it may seem invasive to some, the measures in place are designed to strike a balance between security and privacy, ensuring that individuals can go about their daily lives without fear of harm or danger.