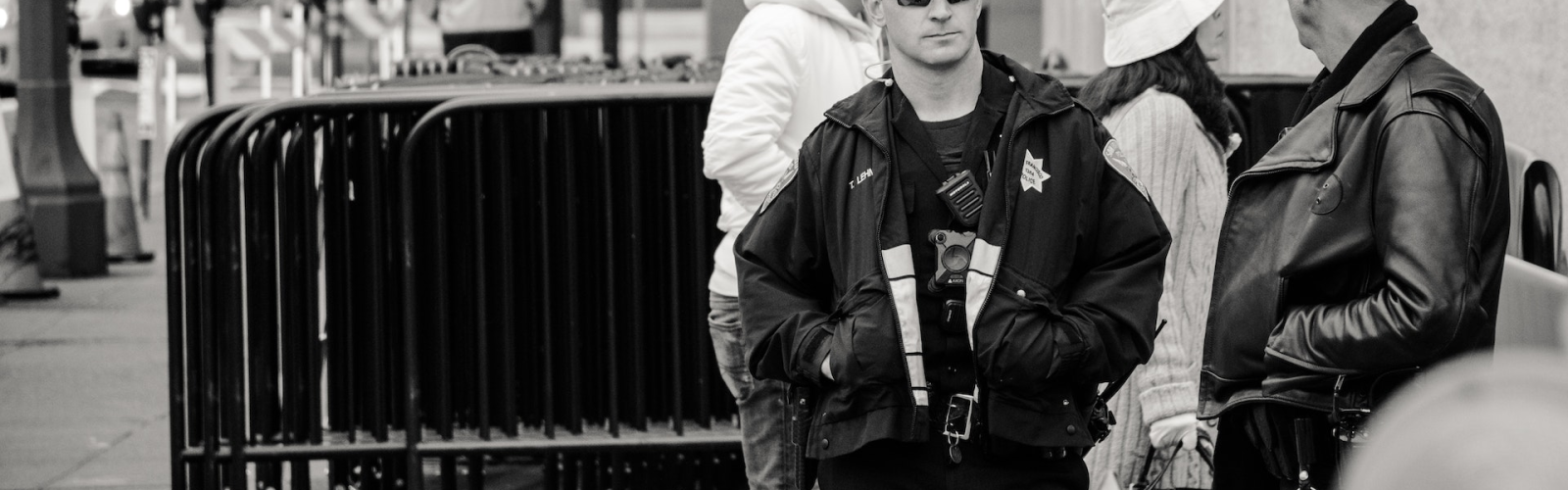
In recent years, the development of new technologies has brought significant changes to the way security agencies operate. From new surveillance tools to advanced cybersecurity measures, these technologies have helped improve the efficiency and effectiveness of security agencies in protecting citizens and preventing criminal activities.
One of the most significant advancements in security technology has been the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms. These technologies have enabled security agencies to analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns and anomalies, and detect potential threats in real-time. For example, AI-powered facial recognition technology is now widely used by law enforcement agencies to track down suspects and prevent crime.
Another technology that has revolutionized the security industry is the Internet of Things (IoT). With the increasing number of connected devices, security agencies can now monitor and control physical environments more effectively. Smart security cameras, for instance, can provide real-time footage of public areas, enabling law enforcement to quickly respond to incidents and identify suspects.
However, with the increased use of these technologies, concerns over privacy and data protection have also grown. There are fears that the use of facial recognition technology could lead to the violation of civil liberties and the creation of a surveillance state. Moreover, IoT devices have been known to have security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by cybercriminals.
To address these concerns, security agencies have been working to develop better cybersecurity measures. Advanced encryption technologies and multi-factor authentication systems have been implemented to protect sensitive data from cyber threats. Additionally, privacy laws and regulations have been put in place to ensure that the use of new technologies by security agencies is not invasive and respects individuals' rights.
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the interconnection of physical devices, vehicles, buildings, and other objects with sensors, software, and network connectivity to collect and exchange data. This network of devices is designed to make our lives more convenient, efficient, and productive by automating processes and providing real-time information.
IoT devices can be found in various industries, including healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, transportation, and smart homes. For example, in healthcare, IoT devices can monitor patients' vital signs and send data to healthcare providers, allowing for remote monitoring and timely intervention. In manufacturing, IoT devices can be used to optimize production processes and minimize downtime by detecting equipment malfunctions before they occur. In agriculture, IoT sensors can monitor soil moisture and temperature levels, enabling farmers to optimize crop yields and reduce water usage.
The connectivity of IoT devices allows them to communicate with each other, share data, and perform tasks autonomously, creating a network of smart devices that can operate efficiently without human intervention. This is made possible through the use of machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence (AI) that enable IoT devices to analyze data and make decisions based on that data.
However, the increased use of IoT devices also presents new security risks, as these devices can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks that can compromise sensitive data and cause system malfunctions. To address these risks, manufacturers of IoT devices have been working to improve device security by implementing encryption and authentication protocols to protect data transmission and user privacy.
Overall, the IoT has the potential to transform the way we live and work by enabling greater automation, efficiency, and productivity. As the number of IoT devices continues to grow, it is important to ensure that they are secure and that privacy concerns are addressed to fully realize the benefits of this emerging technology.
In conclusion, the development of new technologies has brought both benefits and challenges to security agencies. While AI, IoT, and other technologies have helped improve security operations, concerns over privacy and data protection must also be addressed. By developing and implementing appropriate security measures, security agencies can continue to harness the power of new technologies while ensuring the protection of citizens' rights and freedoms.